BDBM50152119 CHEMBL3775362
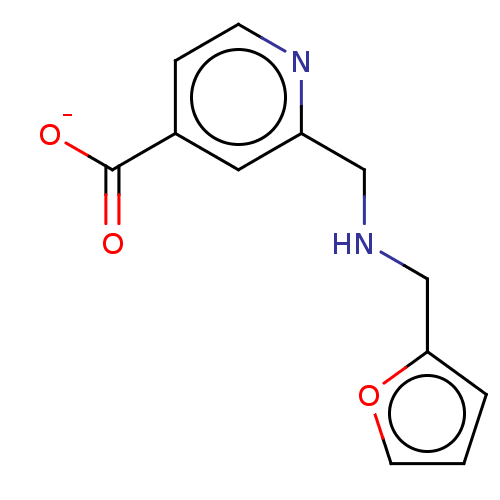
SMILES [Li+].[O-]C(=O)c1ccnc(CNCc2ccco2)c1
InChI Key InChIKey=RLSMOWZMCXMDDN-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Data 4 IC50
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
 Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50152119
Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50152119
TargetLysine-specific demethylase 5B(Homo sapiens (Human))
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 40nMAssay Description:Inhibition of KDM6B (unknown origin) using biotin-H3K27me3 (21 to 44 residues) as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition m...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetLysine-specific demethylase 5C(Homo sapiens (Human))
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 30nMAssay Description:Inhibition of KDM5C (unknown origin) using biotin-H3K4me3 as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition measured after 20 mins...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetLysine-specific demethylase 4A(Homo sapiens (Human))
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 300nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human N-terminal His-tagged KDM4A (1 to 359 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli using biotin-H3K9me3 as substrate preincubated for ...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetLysine-specific demethylase 4B(Homo sapiens (Human))
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
The Institute Of Cancer Research
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 170nMAssay Description:Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal GST-tagged KDM4B (1 to 500 residues) expressed in baculovirus infected sf9 cells using biotin-H3K9me3 as s...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair