TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
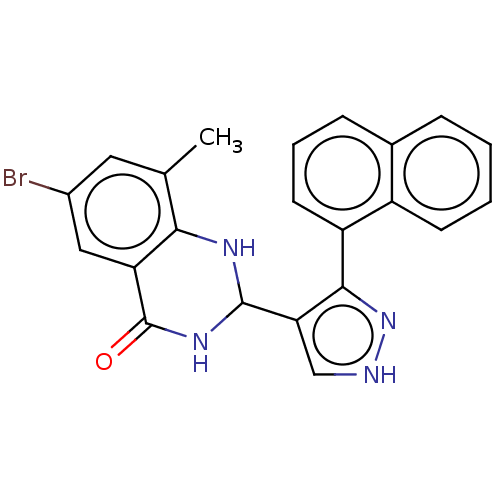
Affinity DataIC50: 320nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents treated extracellularly after 60 secs by w...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
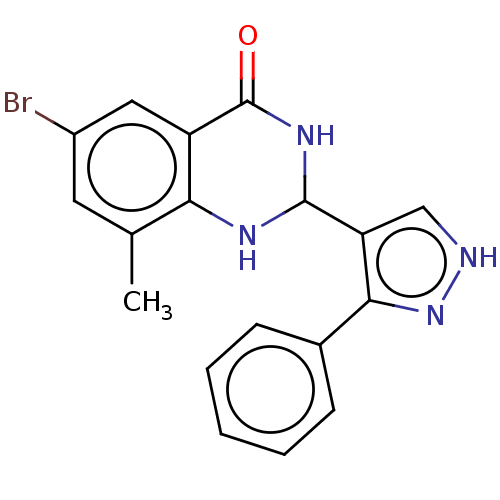
Affinity DataIC50: 1.70E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents by whole cell patch clamp electrophysiolog...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
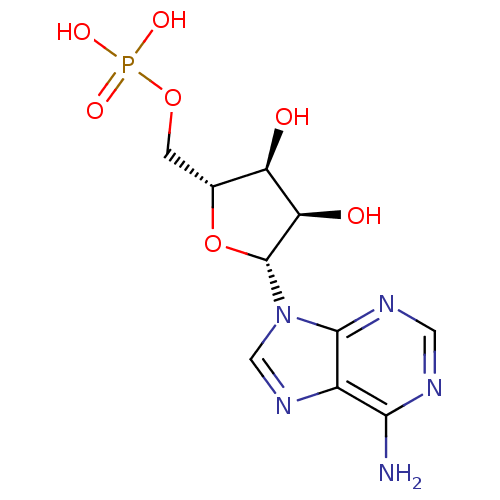
Affinity DataIC50: 1.70E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in H2O2-induced intracellular calcium flux after 30 mins by Fluo4-AM dye ba...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 3.70E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents treated extracellularly after 60 secs by w...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 8(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 3.90E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM8 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in H2O2-induced intracellular calcium flux after 30 mins by Fluo4-AM dye ba...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 4.00E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents treated extracellularly after 60 secs by w...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 4.60E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents treated extracellularly after 60 secs by w...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 5.10E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents treated extracellularly after 60 secs by w...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetTransient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2(Homo sapiens (Human))
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Peking University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 7.00E+4nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TRPM2 assessed as reduction in ADPR-induced channel currents by whole cell patch clamp electrophysiology methodMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair