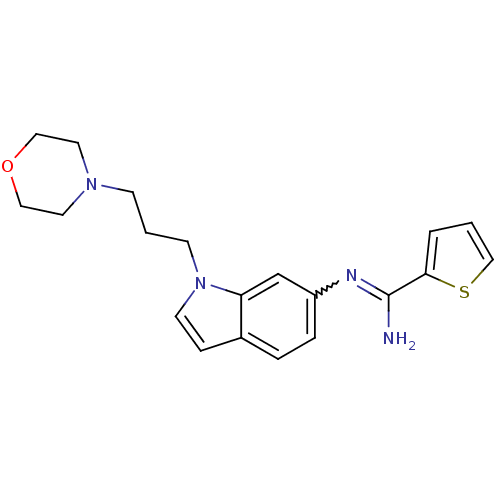
Affinity DataIC50: 700nMAssay Description:Enzyme assay using recombinant human inducible NOS (iNOS), human endothelial constitutive NOS (eNOS) or human neuronal constitutive NOS (nNOS).More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 700nMAssay Description:Inhibition of recombinant human nNOS expressed in baculovirus infected insect Sf9 cells assessed as conversion of [3H]-L-arginine into [3H]-L-citrull...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 2.83E+4nMAssay Description:Inhibition of recombinant human eNOS expressed in baculovirus infected insect Sf9 cells assessed as conversion of [3H]-L-arginine into [3H]-L-citrull...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 2.83E+4nMAssay Description:Enzyme assay using recombinant human inducible NOS (iNOS), human endothelial constitutive NOS (eNOS) or human neuronal constitutive NOS (nNOS).More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 8.20E+4nMAssay Description:Inhibition of recombinant human iNOS expressed in baculovirus infected insect Sf9 cells assessed as conversion of [3H]-L-arginine into [3H]-L-citrull...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair